The cis-double bonds in the unsaturated fatty acids introduce a kink in their shape which makes it more difficult to pack their molecules together in a stable repeating array or crystalline lattice. The Saturated Hydrocarbons or Alkanes.

Figure 3 From Saturated Vs Unsaturated Hydrocarbon Interactions With Carbon Nanostructures Semantic Scholar

Organic Chemistry Chapter 22 Vocabulary Organic Chemistry Hydrocarbons

Solved Unsaturated Hydrocarbons Section 13 1 13 1 Classify Chegg Com
Aliphatic compounds may be saturated or unsaturated.

Saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons. A unsaturated Even though rings only contain single bonds rings are considered unsaturated b unsaturated c saturated d unsaturated 2. A hydrocarbon that has at least one double or triple bond between carbon atoms is an unsaturated hydrocarbon. 258 explain that cracking involves the breakdown of larger saturated hydrocarbons alkanes into smaller more useful ones some of which are unsaturated alkenes.
CCEA Double award science. An acyclic saturated hydrocarbon with the general formula C n H 2n2Also called paraffin. Aromatic compounds originally named because of their fragrant properties are unsaturated hydrocarbon ring structures that exhibit special properties including unusual stability.
Saturated Hydrocarbon A hydrocarbon is said to be saturated if it contains only CC single bonds. On heating the saturated solution the solubility of that particular solute increases in the given solvent. Saturated in this case means that each carbon atom is bonded to four other atoms hydrogen or carbonthe most possible.
They contain sp 2 or sp hybridized carbons. The configuration of an unsaturated carbons include straight chain such as alkenes and alkynes as well as branched chains and aromatic compounds. Ii unsaturated and iii aromatic hydrocarbons.
Some hydrocarbons prevent the rotation of the atoms about the bond by locking them into specific structural formations. Saturated solution on heating becomes unsaturated whereas an unsaturated solution becomes saturated upon cooling. This means alkenes and alkynes more likely to readily react with a chemical reagent than an alkane.
If different carbon atoms are joined together to form open chain of carbon atoms with single bonds they are termed as alkanes as you have already studied in Unit 12. Alkanes and alkenes both form homologous series of hydrocarbons but. Alkanes are saturated their carbon atoms are only joined by C-C single bonds alkenes are unsaturated they contain at least.
Hydrocarbons Class 11 Notes Chemistry Chapter 13 Hydrocarbon A compound of carbon and hydrogen is known as hydrocarbon. Having only single bonds is defined as a saturated hydrocarbon. Further Chemical Reactions Rates and Equilibrium Calculations and Organic.
CH 4The Lewis structure of methane can be generated by combining the four electrons in the valence shell of a. Experiment 3 Hydrocarbons Page 2 Hydrocarbons may be saturated or unsaturatedA saturated hydrocarbon is one that is maxed out in terms of the number of hydrogens that can be present given the number of carbons in the compound. It is impossible to add more hydrogen atoms to the compound so it is saturated with hydrogen.
Saturated hydrocarbons can be distinguished from unsaturated hydrocarbons in the laboratory because saturated hydrocarbons are less chemically active reactive than unsaturated hydrocarbons. Hydrocarbons in Fuel Hydrocarbons containing between six and 10 carbon molecules are the top components of most fuels regardless of whether they are alkanes alkenes or cyclic. Interconversion of Saturated and Unsaturated Solution.
Saturated hydrocarbon contains mainly of alkanes which are open chain hydrocarbons containing carbon-carbon single bond. Describe the reactions characteristic of saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons Identify structural and geometric isomers of hydrocarbons The largest database 1 of organic compounds lists about 10 million substances which include compounds originating from living. Fatty acids may be saturated or unsaturated.
Hydrocarbons with only carbon-to-carbon single bonds CC and existing as a continuous chain of carbon atoms also bonded to hydrogen atoms are called alkanes or saturated hydrocarbons. As a result of this more solute can be dissolved into the solvent. You will learn more about these different types of hydrocarbons later in this chapter.
Unsaturated hydrocarbons are hydrocarbons that have double or triple covalent bonds between adjacent carbon atomsThe term unsaturated means more hydrogen atoms may be added to the hydrocarbon to make it saturated ie. Main groups of hydrocarbons. Definitions of organic compounds.
An organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Unsaturated hydrocarbons are more likely to be solid than their saturated counterparts as are cyclic hydrocarbons. 2516 determine the presence of a CC using bromine water.
Consisting all single bonds. On the other hand if carbon atoms. Vinegar is an unsaturated acetic acid solution in water.
Saturated hydrocarbons contain carbon-carbon and carbon-hydrogen single bonds. Alkanes are described as saturated hydrocarbons while alkenes alkynes and aromatic hydrocarbons are said to be unsaturated. Saturated Hydrocarbons Alkanes and Cycloalkanes.
Contain more hydrogen atoms than the corresponding unsaturated hydrocarbons. There are no double or triple bonds in the molecules. If the molecular structure is given the easiest way to solve is to count the number of double bonds triple bonds andor rings.
Most reactions of organic compounds take place at or adjacent to a functional groupIn order to establish a baseline of behavior against which these reactions may be ranked we need to investigate the reactivity of. Ethane CH3CH3 Unsaturated Hydrocarbon Aromatic Hydrocarbon Benzene and its derivatives are called aromatic compounds. For hydrocarbons the DBE or IHD tells us the number of rings andor extra bonds in a non-saturated structure which equals to the number of hydrogen pairs that are required to make the structure saturated simply because joining two elements to form a ring or adding one extra bond in a structure reduces the need for two Hs.
Saturated and Unsaturated Aliphatic Hydrocarbons. Most of the time the bond exists in the form of a covalent bond. The main difference between saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbon is that saturated hydrocarbons contain only single covalent bonds between carbon atoms whereas unsaturated hydrocarbons contain at least one double or triple covalent bond in the main chain.
In a fatty acid chain if there are only single bonds between neighboring carbons in the hydrocarbon chain the fatty acid is said to be saturated. Adding a spoonful of sugar to a hot cup of coffee produces an unsaturated sugar solution. The higher melting points of the saturated fatty acids reflect the uniform rod-like shape of their molecules.
Saturated fatty acids are saturated with hydrogen since single bonds increase the number of hydrogens on each carbon. All carbon atoms are sp 3 hybridized in these compounds. Alkanes hydrocarbons in which all the bonds are single have molecular formulas that satisfy the general.
Reading Check Explain the origin of the terms saturated and unsaturated hydrocarbons. Examples include alkanes and cycloalkanes. An unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carboncarbon double bond with the general formula C n H 2n.
Examples of Unsaturated Solutions. Compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen are known as hydrocarbonsThose that contain as many hydrogen atoms as possible are said to be saturatedThe saturated hydrocarbons are also known as alkanes. The simplest alkane is methane.
Contain fewer hydrogens than the corresponding saturated hydrocarbon. Hydrogenation can be used to create a fully saturated ring system.

Ppt Unsaturated Hydrocarbons Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6511501
Difference Between Saturated And Unsaturated Hydrocarbons Definition Structure Types Properties
Difference Between Saturated And Unsaturated Compounds Definition Explanation Examples And Differences
What Are Hydrocarbons Give Examples B Give The Structural Differences Between Saturated And Unsaturated Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community
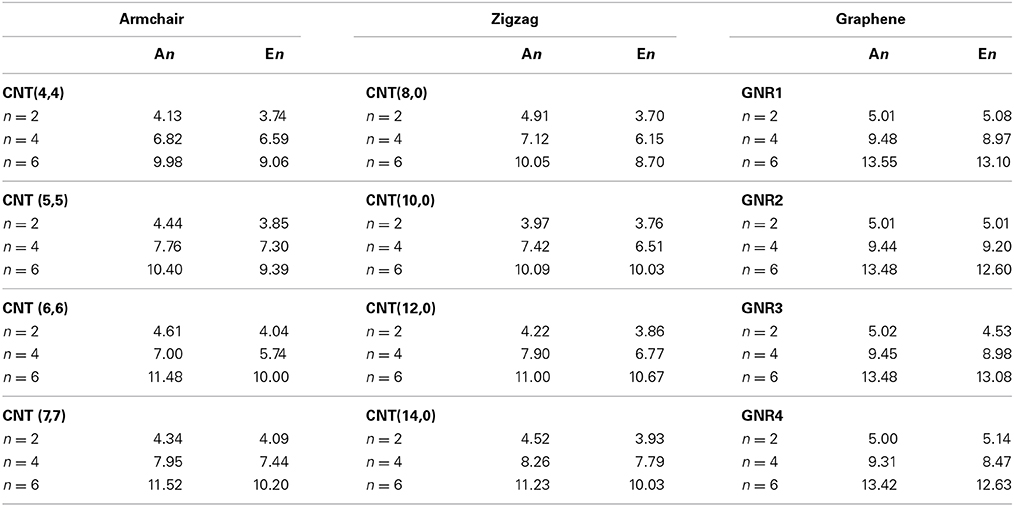
Frontiers Saturated Vs Unsaturated Hydrocarbon Interactions With Carbon Nanostructures Chemistry

Petroleum Refining Saturated Molecules Britannica

Saturated And Unsaturated Compounds Alchetron The Free Social Encyclopedia

Possible Orientations S And T Of The Unsaturated Hydrocarbons On Cnss Download Scientific Diagram